Spine Center
When Should You See a Spine Specialist?
Our spines are complex support structures that make all kinds of movements possible. Running from the top of the neck to the base of the tailbone, the spine is composed of thirty-three bones, called vertebrae, which are divided into five regions: cervical, thoracic, lumbar, sacral and coccygeal. You can learn more about the anatomy of the spine here.
Different kinds of spinal injuries - and how they should be treated - can be categorized by the amount of time and the extent to which they affect you. Acute spine pain, which is often caused by a traumatic fall or heavy lifting, can last up to 6 weeks. In these cases, a chiropractor may be able to help treat acute back pain, but it's still important to see a spine doctor to determine the root issue and treat it effectively.
Chronic spine pain, on the other hand, typically lasts more than 3 months. Persistent or lingering conditions should be treated by an expert orthopaedist at Resurgens. This is especially true if you experience problems with bladder or bowel function, numbness around the genitals, trouble sleeping, or pain accompanied by fever, chills, or sweats.
What Causes Back or Neck Pain?
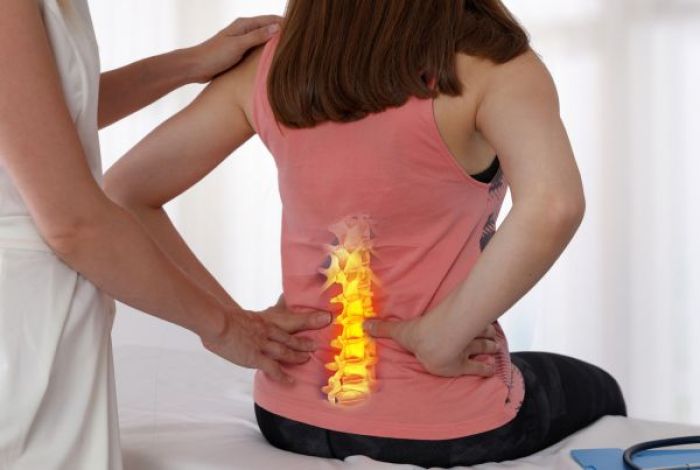
When you suffer a spinal injury, the consequences can range from mild pain and discomfort to debilitating pain and restricted movement. If you experience any level of discomfort in your spine, it's important to see a spine doctor to determine the cause and treat it effectively.
Conditions like strains of the lower back muscles, herniated discs, or sciatica, which is the compression or irritation of your spine's nerve roots, are all common culprits behind spine pain or limited motion. However, other serious, degenerative conditions, such as spondylosis, could be affecting you as well.
Learn more about the anatomy of your spine to better understand where you might be suffering a potential spine condition. This will help you discuss your condition with your spine doctor.
How Resurgens Diagnoses Back and Neck Pain
When you suffer from a spine injury of any kind, it can greatly impact your ability to do even the simplest tasks. That's why it is critical for patients to work with the Resurgens Spine Center to immediately identify the underlying conditions causing their back or neck pain, and then develop an appropriate treatment plan.
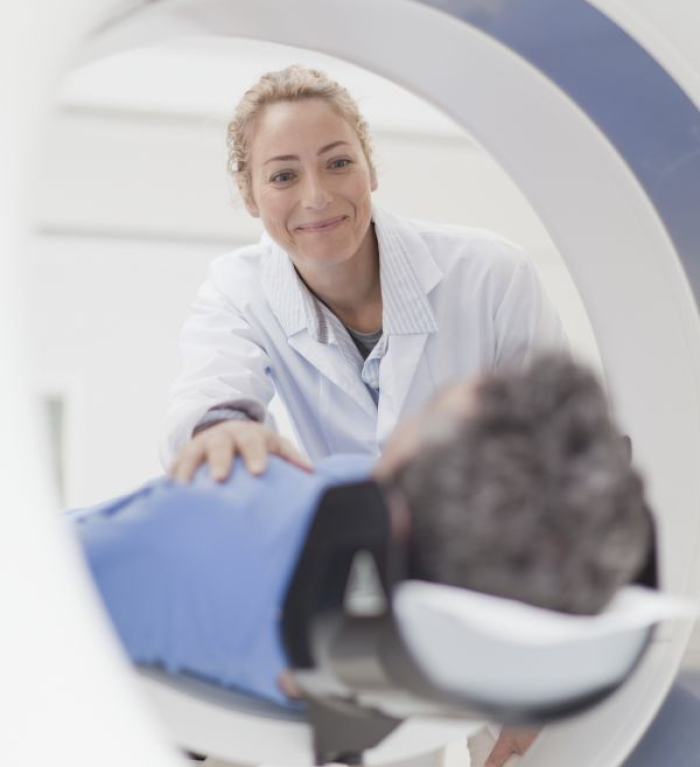
The Resurgens Orthopaedic Spine Center uses a variety of diagnostic tests to help identify the specific nature of your injury or condition. Visit our educational portal to learn more about the state-of-the-art diagnostic tests and technology Resurgens Orthopaedics uses to diagnose back and neck conditions.
Non-Surgical and Surgical Treatment for Spine Pain
Depending on the severity and location or your spine condition, various treatment solutions are available - both non-surgical and surgical. Our Resurgens physicians will always work with you to decide the best treatment option based on your unique situation and lifestyle, while also ensuring conservative measures are attempted before considering surgical procedures.
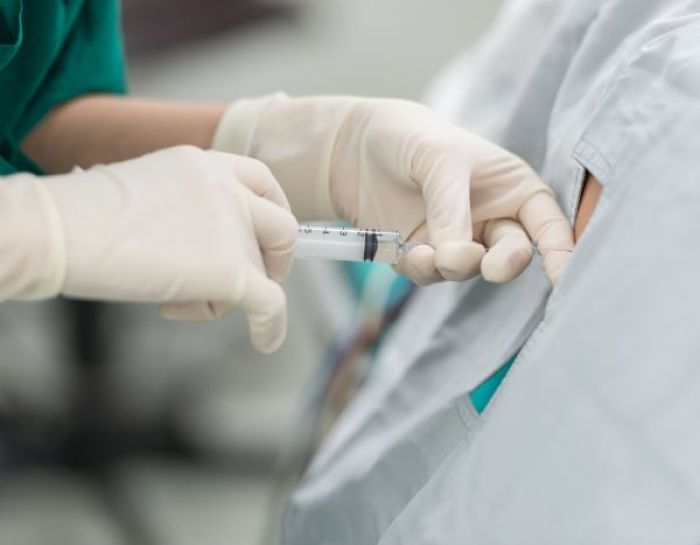
It's important to know that not every visit to an orthopaedic spine surgeon results in surgery. Non-surgical solutions are available, such as spine injections and spine therapy. Learn more about our non-surgical solutions and spine rehabilitation treatment options and talk with your spine specialist to find out if any of these options are right for you.
More critical spine conditions or injuries could require surgical solutions. While we will ensure less intensive solutions have been explored before pursuing a surgical treatment plan, our team of spine surgery specialists at Resurgens Spine Center are trained in the latest surgical techniques, including minimally-invasive spine surgery and outpatient surgical procedures. Read about our surgical spine treatments here.
Spine FAQs
We understand how consequential a spine injury, no matter how big or small, can be for someone's daily life. A spine treatment procedure can be just as impactful, which is why our spine physicians have answered the frequently asked questions surrounding spine pain, conditions, and procedures.
Check out our spine FAQ to find out more.