Rheumatoid Arthritis
Types, Symptoms & Treatment
What You Need To Know About Rheumatoid Arthritis
What Is Rheumatoid Arthritis?
A chronic autoimmune disease found in the joints, rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is an autoimmune disease. Your immune system attacks healthy cells in your body by mistake, causing painful swelling in the affected parts of the body.Rheumatoid arthritis can appear in any of your joints, including those in the fingers and hands, wrists, knees, and feet.
When healthy, cartilage in your joints serves an important purpose; it acts as a buffer between your bones, preventing them from scraping against each other and instead providing a shock-absorbing boundary. When rheumatoid arthritis is present, cartilage is more easily damaged, which can cause discomfort and pain. Bones will wear down and erode when the cartilage is damaged, resulting in chronic pain, deformed bones and joints, and eventually can lead to the fusion of your joints, as part of your body's efforts to protect itself from irritation.
Specific cells in your immune system aid this process. These substances are produced in your joints but also circulate and cause symptoms throughout your body. As a side effect to this, other tissues in your body may be affected, too — including your eyes and lungs.
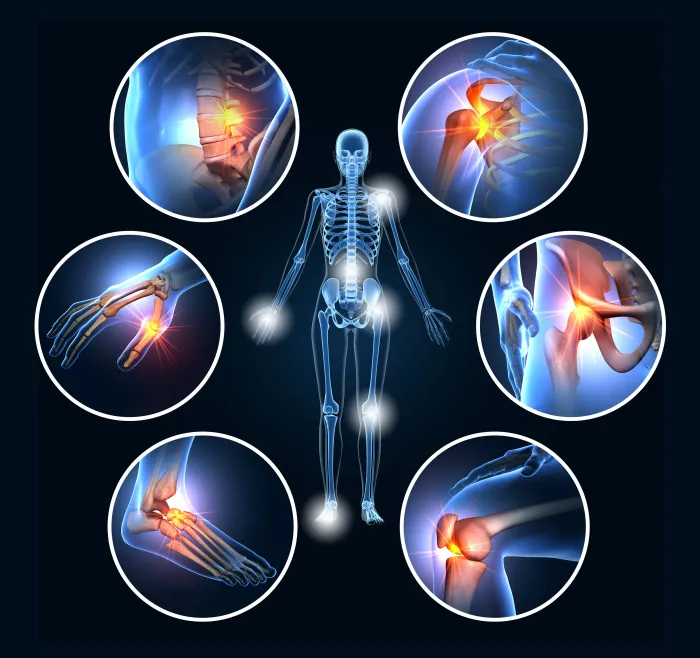
Common Areas for Rheumatoid Arthritis
Although rheumatoid arthritis can occur in any joint in the body, it's most commonly found in the hands, feet, and shoulders.
Hand Rheumatoid Arthritis
You may have heard of rheumatoid arthritis of the hand most often. It's one of the most commonly affected areas, and it's regularly found in both hands at once rather than just one. Rheumatoid arthritis of the hand can severely interfere with normal hand function, and significantly impact a person's quality of life.
Symptoms can include stiffness, pain in the joints of the hand (especially the base and middle of the fingers, the hand, and the wrist), inflamed knuckles, and misaligned fingers angled away from the thumb. Non-surgical treatments include orthopedic gloves.
Foot Rheumatoid Arthritis
More than 90% of people with rheumatoid arthritis develop foot and ankle symptoms during their lifetime. In 20% of patients, ankle arthritis is one of the first signs of the disease. It commonly affects the feet and ankles on both sides of the body at the same time, rather than just one.
Symptoms of rheumatoid arthritis in the feet and ankles include stiffness, collapsed foot arches, calluses and sores, unusual warmth in the feet, abnormal toe positioning, and lumps around the joints. Common changes in foot shape as a result of rheumatoid arthritis include bunions, flat feet, and claw toes. Non-surgical treatments include orthopedic shoes and the assistance of a cane.
Shoulder Rheumatoid Arthritis
The joints in the shoulder are some of the more unique and sensitive joints in the body. Because of this, rheumatoid arthritis of the shoulder can be particularly debilitating.
Symptoms of rheumatoid arthritis of the shoulder include stiffness, bone spurs, limited range of motion, popping and grinding sensations, and other limitations. Non-surgical treatments include physical therapy, an adjustment of daily activities, and increased rest.
What Causes Rheumatoid Arthritis?
Genetics
Chemical or environmental factors
Chemical or Environmental Triggers
Hormonal Imbalances
Rheumatoid Arthritis Symptoms
The hallmark rheumatoid arthritis symptoms in the body are pain, stiffness, swelling, unusual or excessive warmth, and visible joint deformity. Other common signs of rheumatoid arthritis include:
- Extreme fatigue and tiredness unexplained by other causes
- Weakness Persistent stiffness after sitting for long periods or sleeping
- Fever
- Loss of appetite
- Decreased or depleted energy
- Anemia, or low red blood cell count
- Lumps or nodules
- Calluses or sores
- Bone spurs
- Weight gain
- High blood pressure and high cholesterol
- Diabetes
Because rheumatoid arthritis is an autoimmune disease, other parts of the body can be directly affected. These include:
- Dryness, redness, pain, and sensitivity in the eyes
- Scarring and shortness of breath in the lungs
- Inflamed blood vessels causing damage in the heart and other organs
- Dryness, gum inflammation, and infection in the mouth
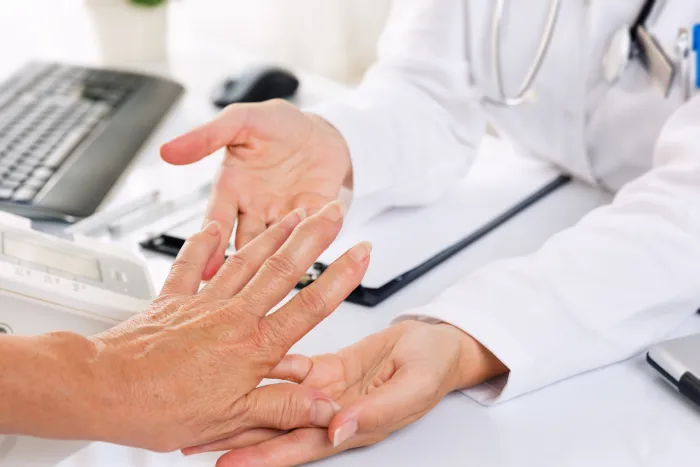

How Is Rheumatoid Arthritis Diagnosed?
A Resurgens rheumatologist will start your appointment with a routine physical exam. They will ask you about any joint pain, tenderness, or stiffness — including how long those symptoms have been present, when they started, and how they affect your quality of life. Be sure to share any information you have on family members with rheumatoid arthritis or other autoimmune diseases.
During the physical examination, your doctor will look for signs of joint inflammation and other bumps and lumps you may not have noticed previously. Depending on their findings, your doctor will recommend either an X-Ray or an ultrasound to look for signs of bone erosion and damage.
Blood tests can also be performed to look for signs of inflammation. These tests will measure the erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ECR) in your joints, your C-reactive protein levels, and your red blood cell count.
- In order to receive a diagnosis for rheumatoid arthritis, you must have most of the following:
- Visible inflammation in two or more large joints, such as the shoulder or ankle
- Visible inflammation in multiple small joints, including the fingers and toes
- Elevated C-reactive protein (CRP)
- Elevated erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ECR)
- A positive biomarker, such as the rheumatoid factor (RF) or cyclic citrullinated peptides (CCP) antibodies
- A long history of symptoms, at least longer than six weeks
Patients diagnosed with rheumatoid arthritis don't necessarily have every symptom or criteria required for diagnosis.
Rheumatoid Arthritis Treatment
There are several types of treatment available for rheumatoid arthritis, depending on where you're experiencing pain and the severity in which it affects your life and well-being. A Resurgens physician can diagnose and work with you to prepare the best treatment option for your needs and lifestyle. This can be a non-surgical treatment, a surgical treatment, or a combination of the two.
Regardless of which treatment you choose, the goal of treatment is to reduce inflammation and relieve symptoms while preventing further damage to joints and complications to the body as a whole.
Non-Surgical Treatment
There are a number of non-surgical treatment options for rheumatoid arthritis. Pain relievers are amongst the most common choices for treatment, and they include:
- NSAIDs (non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs), such as ibuprofen (Advil), naproxen (Aleve), and aspirin
- DMARDs (disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs), such as methotrexate (Trexall), sulfasalazine (Azulfidine), and hydroxychloroquine (Plaquenil)
- Corticosteroids, such as prednisone and cortisone
If you'd rather not treat your rheumatoid arthritis with the above medications, biologics are another possible treatment. Biologics, or biologic response agents, are built to target the molecules causing painful inflammation in your joints.
Surgical Treatment
Depending on the severity of your symptoms and pain, a surgical treatment option may be recommended. Surgery for rheumatoid arthritis may be able to restore function back to joints like hands and feet. Other surgeries include hip replacements and knee replacements.
During these surgery treatments, orthopedic surgeons remove the damaged parts of affected joints and replace them with metal or plastic pieces. In order to keep these pieces in place, bone cement is often used to encourage the bones to form a tight bond.
Following surgery, physical therapy will help you gain movement back in your joints and stabilize and strengthen other areas of the body to support the procedure. No matter what you choose, your doctor will be the best person to discuss your individualized treatment plan with you.
Finding the best treatment for rheumatoid arthritis starts with a visit to Resurgens Orthopaedics. With over 20 locations in the Metro Atlanta area, it's easy to find a location near you. Book your appointment now to chat with one of our award-winning physicians and get started today!